Veterinary Equipment and Tools: A Complete List For Vets + [PDF Guide]
 If you are planning to establish your own veterinary clinic or hospital, there is a List of Veterinary Equipment, instruments, devices, supplies, and other Vet Tools for veterinarians needed. That’s why we made this Veterinary Equipment List to help all veterinary doctors provide efficient medical care to our patients.
If you are planning to establish your own veterinary clinic or hospital, there is a List of Veterinary Equipment, instruments, devices, supplies, and other Vet Tools for veterinarians needed. That’s why we made this Veterinary Equipment List to help all veterinary doctors provide efficient medical care to our patients.
To know what tools a veterinarian uses to run a new vet clinic, check this List of Veterinary Equipment and Tools For Veterinarians. You will find all you need even If your future practice is a small vet clinic or large hospital as well as These are All Tools For Vets In All types of practices.
List of Veterinary Equipment:
- Veterinary stethoscopes
- Thermometers
- Ophthalmic and aural examinations
- Exam and procedure tables
- Weighing Scales
- IV pumps
- Warming Unit
- Veterinary Ultrasounds
- Digital X-Ray machines
- Anaesthetic Machine
- Monitoring Equipment
- Microscopes
- Veterinary Surgical Instruments
- Emergency Equipment
- Veterinary Dental Equipment
- CT Scanners & MRI
- Centrifugal Machine
- Endoscopic Instrument
- Autoclaves and sterilizers
- Incubators
- Refrigerators
- Boarding Cages
- Lighting
- Other Tools

Stethoscopes are fundamental and one of the most important Vet Tools that all professionals in the medical field need, but the vet needs a specific stethoscope for their practices. Littmann stethoscopes are the most popular.
The Stethoscope is a small, lightweight, and portable tool that has different parts like ear tips, tubes, ear tubes, stem, headset, diaphragm, chest-piece, and bell. The diaphragm or bell picks up the sound created by the animal’s body and passes it to the earpiece.
The stethoscope is essential because it helps us bypass all muscles and fur, and in fact, helps us hear the sounds of the lungs, intestines, and heartbeat. Thanks to this specialized equipment, it is now easy to examine any large or small animal.
Read More: 6 Best Veterinary Stethoscopes For Veterinarians In 2025
2- Thermometers
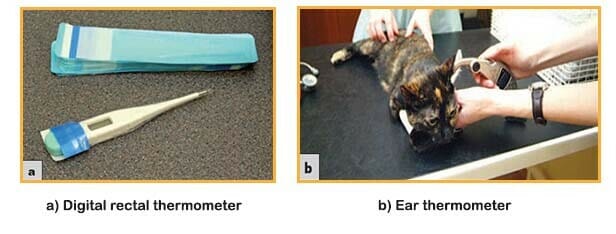
These can be of the traditional glass and mercury type, although they will require a risk assessment and plans for mercury disposal in case of breakage. They must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected between patients. Digital rectal thermometers are accurate and easy to read and are usually supplied with sterile single-use disposable probe covers to avoid cross-infection. Ear thermometers can also be used and suitable models are now available for most small animals. These also use disposable covers to prevent cross-infection. It is better to continue to use the same type of thermometer when monitoring the temperature of an ongoing case, as there can be significant differences in readings between rectal and ear thermometers.
3- Ophthalmic and aural examinations

For ophthalmic examinations a pen torch or Finhoff transilluminator is useful; a hand lens, fluorescein strips and tear test strips should also be to hand in the consulting area. Ophthalmoscopes and auriscopes should be cleaned and checked regularly. Ophthalmoscope and auriscope sets can be either mains- or battery-operated. Wall-mounted mains-operated sets in each consulting room (Figure 6.16) are easy to use, look neat and tidy, are always available, and have the added advantage of never having a flat battery, but attention should be paid to the extending wires. Battery-operated sets are more portable, can be shared between rooms, and taken out on visits, but they need regular checks and supplies of spare batteries available (unless rechargeable batteries are used). They are also easy to leave on, leading to flat batteries, although handsets that come on when they are picked up and automatically switch off when they are put down are now available.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
4- Exam and procedure tables
To examine and treat animals, you will need an examination table in each treatment room. There are different types of exam tables available according to the unique needs of your clinic. You can choose from
- Electric and hydraulic tables
- V-top tables
- Lift tables
The surface of these examination tables is very versatile and flexible and can be adjusted according to the size of your pet patient or the area under examination. These tables are not like standard tables; these are designed for routine disinfection and cleaning.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
5- Weighing Scales

The scales are used in veterinary clinics to measure the weight of each patient because it is used to determine the ideal weight, health, and dose of treatment. The scales are available in a variety of sizes and styles for cats, dogs, horses, and wild animals.
Large scales should be carefully sited so that they are not in a thoroughfare or causing a trip hazard. Smaller scales suitable for cats are better kept in the consulting room to reduce the risk of escape if removing cats from their baskets in the client waiting area. There should also be accurate scales suitable for small and exotic pets, these are also convenient for accurate weighing of food for inpatients.
The new models are pet-friendly with comfortable rubber mats, and an easy-to-read LED display. Some models are portable and offer AC and battery options along with a separate LCD screen.
6-IV pumps
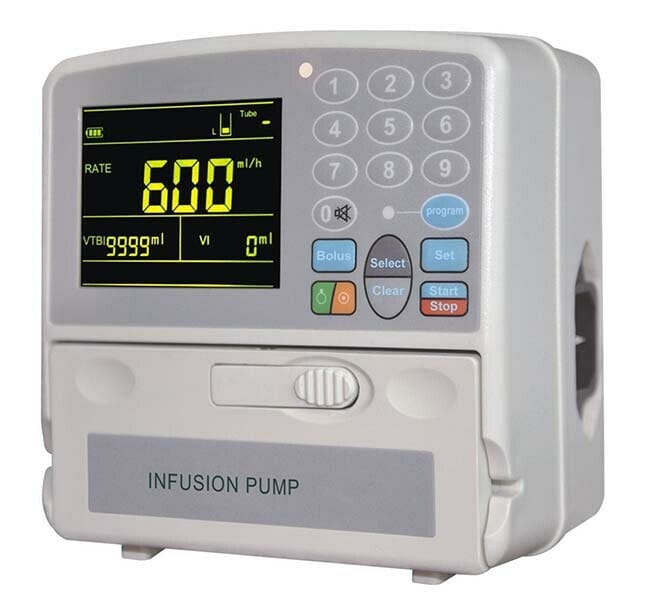

IV pumps are essential equipment used in veterinary clinics to administer medications, fluids, and supplements to patients during surgeries. They are used to control the constant infusion rate for a constant time, ensuring the safe and accurate delivery of drugs.
Syringe pumps offer a more extensive range of delivery modes, with variable syringe sizes. Though more expensive, IV pumps are of high quality and provide extended service, making them a worthwhile investment for any veterinary practice.
7-Warming Unit

A patient warming unit (PWU) is an electronic device that is used to warm a patient in a veterinary clinic. The PWU is used to increase the temperature of a patient, which can improve their comfort and help to reduce the risk of illness. Mostly PWU is used before and after a surgical procedure.
8-Veterinary Ultrasounds
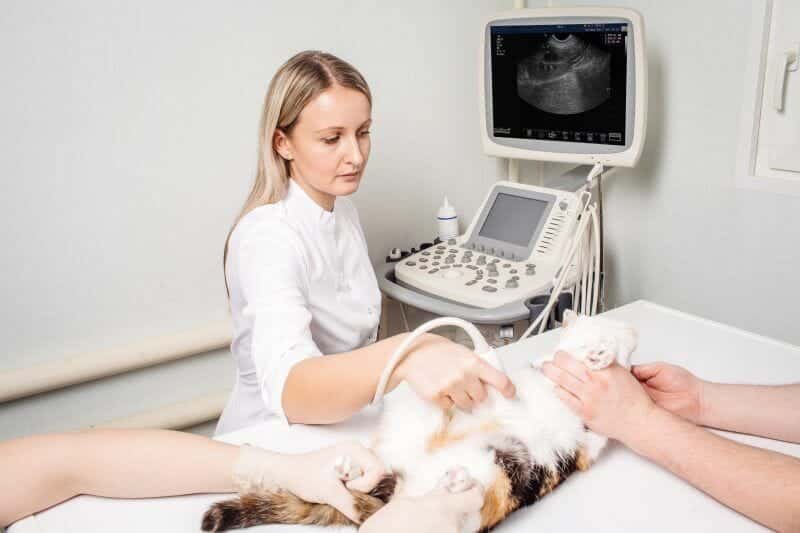
Veterinarians rely on diagnostic imaging techniques to diagnose pets accurately and treat them effectively. Among these techniques, ultrasound is the best diagnostic imaging equipment. It uses sound waves to scan internal images of the animal’s body, which are then displayed on the screen.
Real-time ultrasound machines with external cameras are now available, producing more detailed and broader pictures of the body’s systems and reducing exam time. These images can be shared live with the sonographer via telemedicine.
Portable ultrasound scanners can provide real-time results of the animal’s body condition without worrying about its physical location, making it useful for home visits. They can help examine pets of any size and make quick decisions about administering life-saving medication.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
9-Digital X-Ray machines
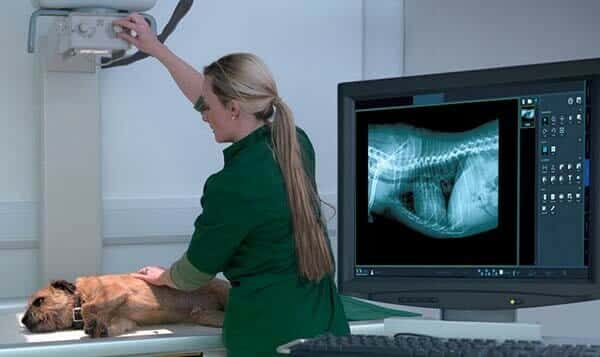
Digital radiology or radiography (DR) can help the vet obtain a clear picture of the muscles, bones, and internal organs without using film and darkroom processing.
These digital images can zoom in and out and focus on minor details that can lead to an accurate diagnosis. The animal will spend more time resting at home than lying on the table for diagnosis. Also, these images can be sent to other vets for further consultation.
Digital radiographs are an essential part of veterinary practices worldwide, and you can select the DR system that best suits your veterinary clinic.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
10-Anaesthetic Machine
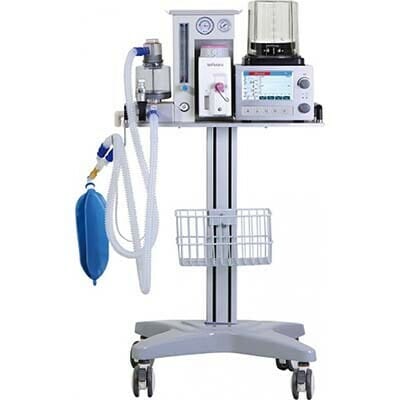
An anesthesia machine is one of the most essential Veterinary Equipment in veterinary clinics as it generates and mixes medical gases to maintain sedation during surgical procedures.
It helps reduce the risk to the animal’s life and is used in combination with monitors to ensure the pet’s vital signs are being monitored. Oxygen is typically used in anesthesia, and maintaining specific protocols is crucial to ensure the animal’s safety.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
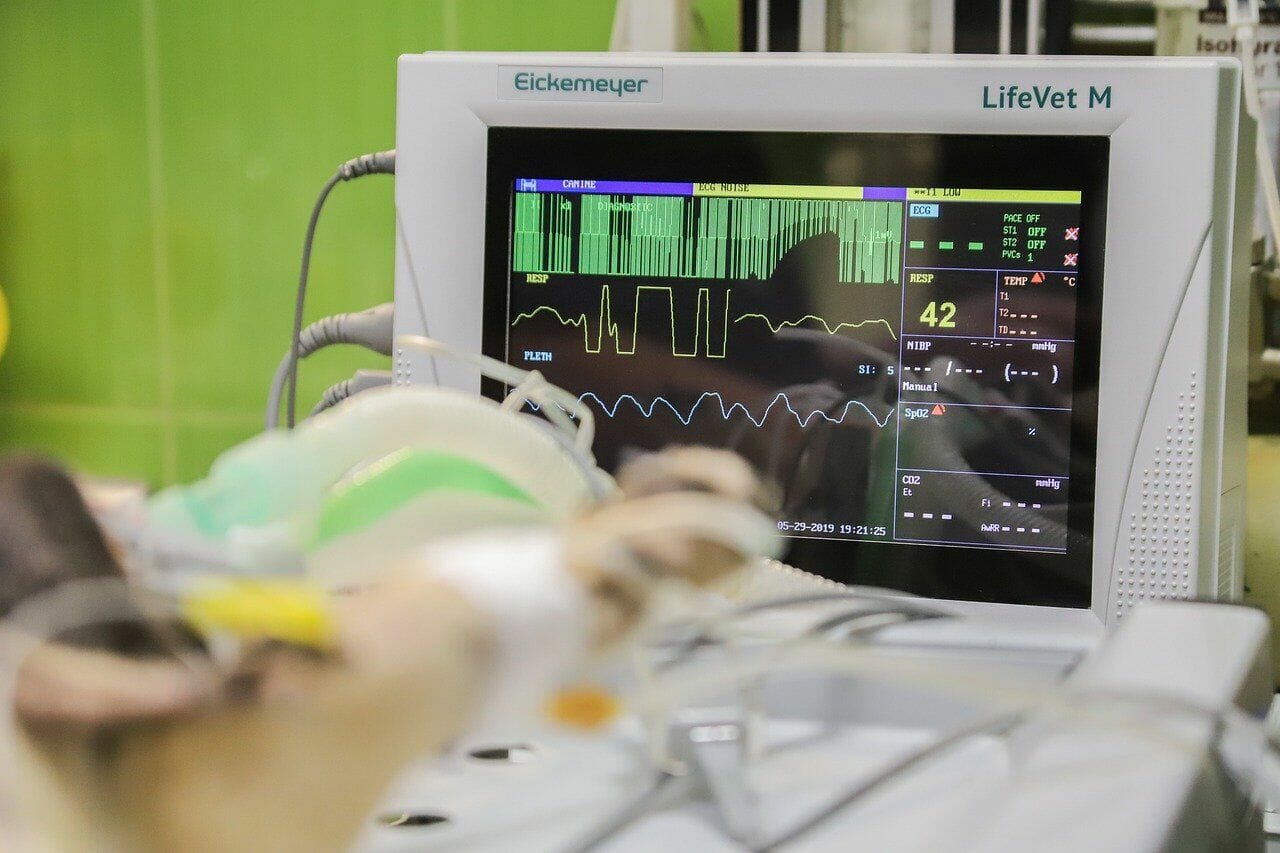
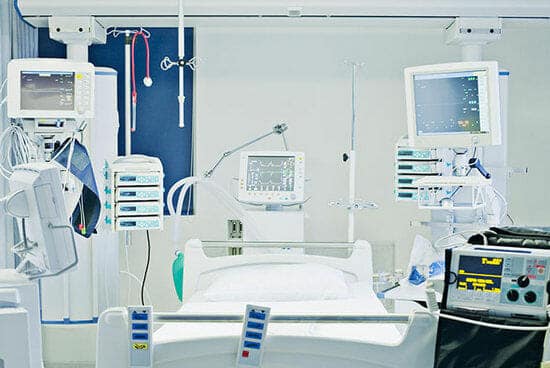
11-Monitoring Equipment
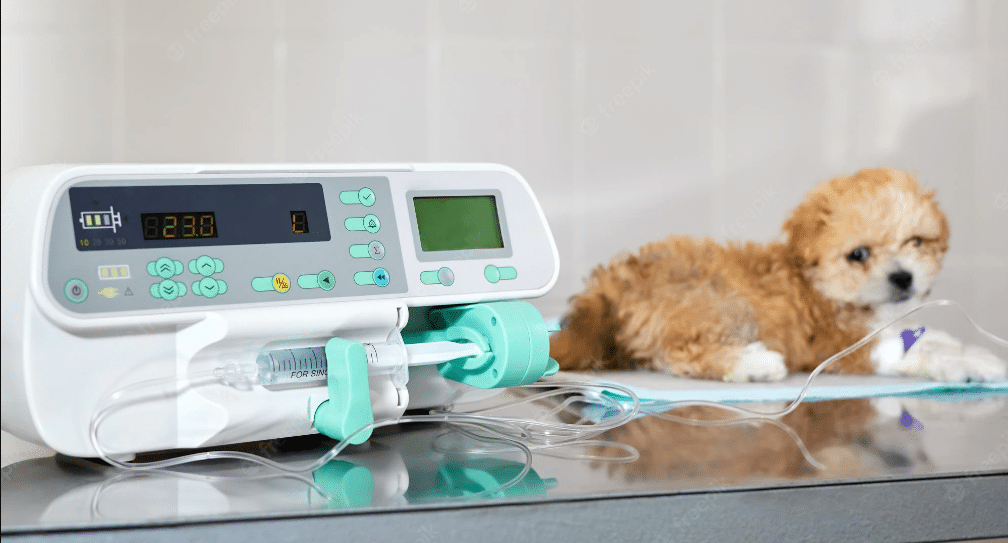
Monitoring equipment can be used in a veterinary clinic to help keep patients safe, healthy, and productive. By using monitors, veterinarians can keep track of important health information like blood pressure and heart rate, as well as vital signs for animals. This can save them time and money in the future when treating patients.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
12-Microscopes

Microscopes are used in veterinary practice for the proper diagnosis and treatment of patients. A microscope can increase the efficiency of a veterinary clinic. They are used to examine patient samples microscopically with the help of certain solutions.
The microscope has significant use in veterinary practices for viewing
- Ear swabs
- Urine sediments
- Fecal parasites
- Blood cytologies
- Differential counts
- Tumor aspirates
- Embryo transfer
- Sperm motilities
- Skin issues
With the advancement of technology, the new microscopes ensure sharp and bright images coupled with new LED lighting, it is easier to examine the sample in the evenings.
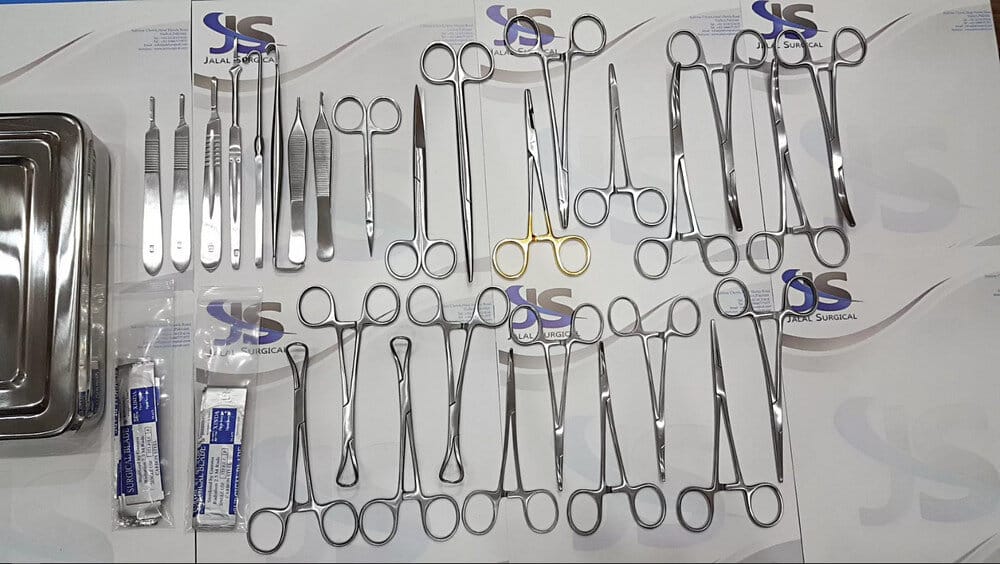
General surgical Instruments
General surgical instruments are the basic instruments of all operations. These must be made with high precision, and therefore, many years of experience must be added to this, to guarantee the best results. When using these instruments it is also important that the user must be experienced to get the best possible results. Here are the general instruments that can be used in surgery.
- Scissors
- Forceps
- Dissecting forceps
- Tissue forceps
- Clamps or hemostats
- Visceral clamps
- Towel clamps
- Scalpel
- Retractors
- Retractors self-retaining
- Needle holder
Others
Orthopedic surgical Instruments
Orthopedic Instruments are tools that are predominantly used by surgeons to carry out Orthopedic surgical operations.
Ophthalmic surgical instruments
Ophthalmic surgical tools are used for carrying out eye related surgeries. Both cornea and lens related surgeries are done with the help of different surgical instruments.
Dental surgical instruments
Dental instruments are very important for every single dental surgery. A dentist may also say that this is the most important thing in their daily work schedule.
Teat surgical instruments
Teats sometimes get damaged and this hinders the cow from providing milk. The teat surgical instruments help to correct all the defects with teats.
Read More: Veterinary Surgical Instruments List: Names, Uses, and Pictures
14-Emergency Equipment

If the consulting room is at a small satellite branch surgery with consulting-only facilities, it is worth considering keeping an ‘emergency box’ at the branch. This can be similar to the anesthetic crash kit, along with intravenous fluids and catheters, endotracheal tubes, and even a small oxygen cylinder and reducing valve, to deal with an emergency that might come in and stabilize a patient before transport to the main surgery.
Read More: 10 Emergency Equipment For Every Veterinary Hospital
Veterinary Books Suggestions
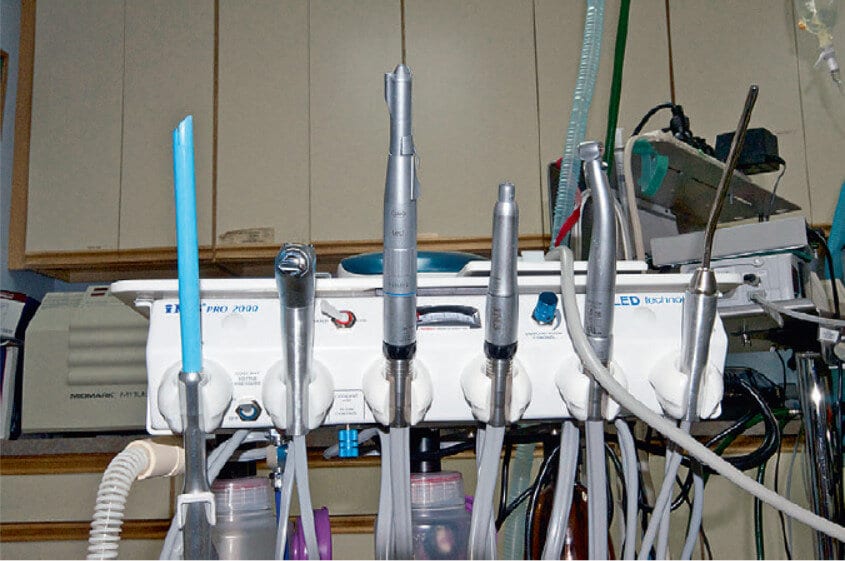
Proper dental care is crucial for animals to prevent infections and other health problems. Veterinary clinics use dental equipment such as toothbrushes, toothpaste, ultrasonic scalers, extraction forceps, bone curettes, tartar remover forceps, and mouth gags to provide the best possible dental care for their patients. An ultrasonic scaler is particularly useful for removing calculus from teeth without causing harm to the animal or their teeth.
Read More: Veterinary Dental Equipment and Instruments: Names and Uses
Veterinary Books Suggestions
16-CT Scanners & MRI
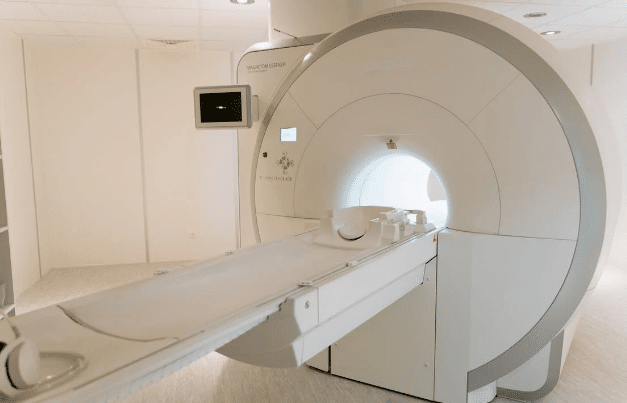
CT scanners are a valuable tool in veterinary clinics to identify tumors and other medical problems, and monitor the animals’ health. They provide a 3D image of the patient’s body, allowing for quicker and more accurate diagnosis and treatment. CT scans also provide a better view of bones and tissues than traditional x-rays.
Veterinary Books Suggestions
17-Centrifugal Machine
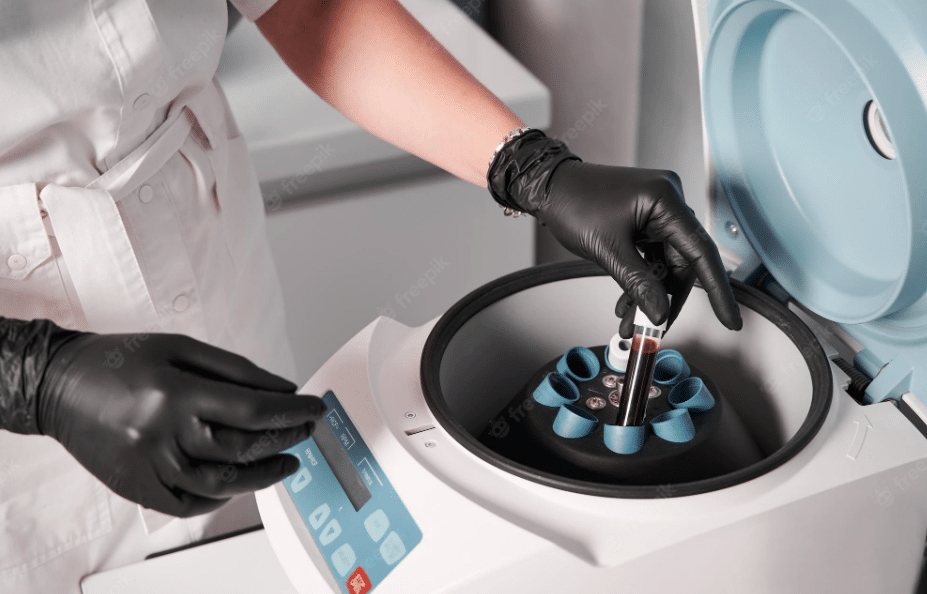

A centrifugal machine is an ideal device in a veterinary clinic. A centrifuge machine helps in separating plasma and serum from blood cells. It also helps in the examination of urine and fecal sedimentation. You can get serum through it for many diagnostic tests in order to diagnose specific diseases by detecting the ag/ab in it.
18-Endoscopic Instrument
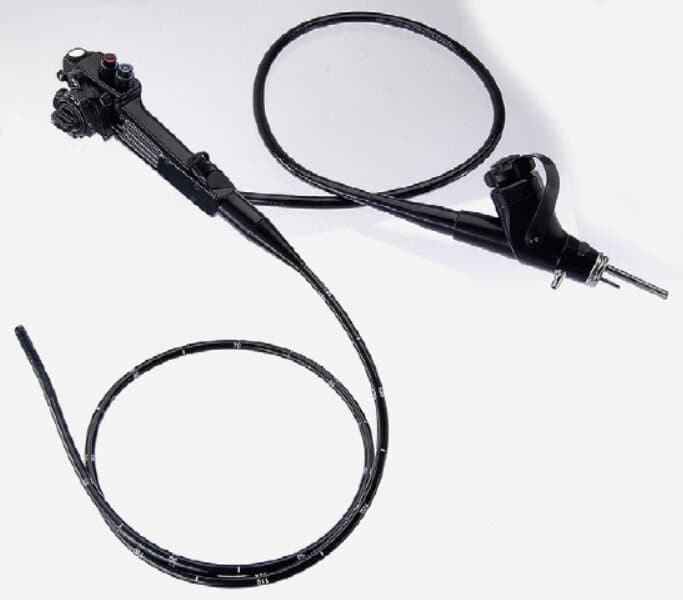

Endoscopy is a method of diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as cancer, gallbladder disease, and other intestinal diseases. It is performed by a specialist, typically a veterinary doctor, using a long, thin tube. Endoscopy is used to view the inside of the stomach and small intestine, as well as the large intestine.
Endoscopes are basically of two types flexible endoscopes and rigid endoscopes. A flexible endoscope is used basically for checking the anatomy of the GI tract. Flexible endoscopy further includes the Fiber scope and video endoscopes. The rigid endoscope is mainly used for the navigation of non tubular areas like joints and body cavities.
19-Autoclaves and sterilizers
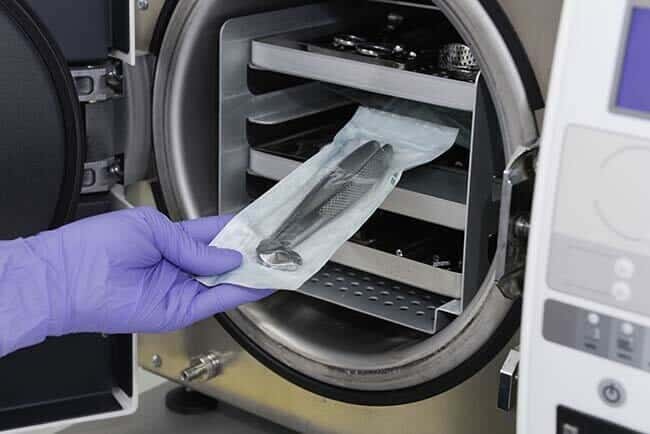

Autoclave and sterilizers are essential in all veterinary clinics for proper sterilization of medical tools. Sterilized and autoclaved tools are necessary for safe and contamination-free surgical work, plus it increases the life of instruments that would otherwise wear out with harsh chemicals.
Autoclaves are available in various sizes, depending on the size of the veterinary clinic. If you are running a high volume clinic, you must purchase a larger unit. Besides, automatic and digital autoclaves allow a faster turnaround than its manual version.
20-Incubators
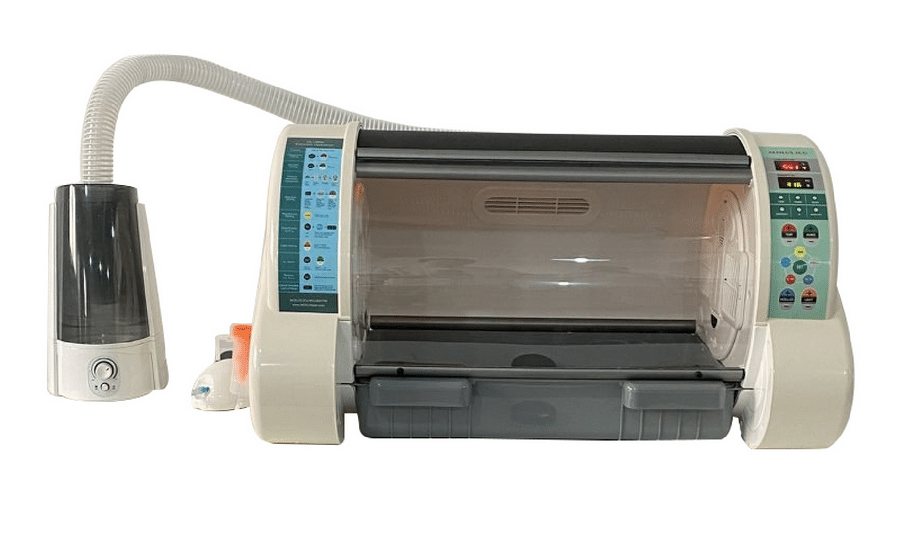

The use of incubators in veterinary clinics can play a vital role in the success of the clinic. In most cases, the incubator is used for bacterial culture and antibiotic sensitivity tests. In veterinary clinics, incubators are a common tool for managing embryos and embryo-derived cells.
To avoid cross-contamination of cultures, incubators are typically equipped with clean detection and isolation equipment. As well, incubators often feature sterile environments in which to maintain the cultures.
21-Refrigerators
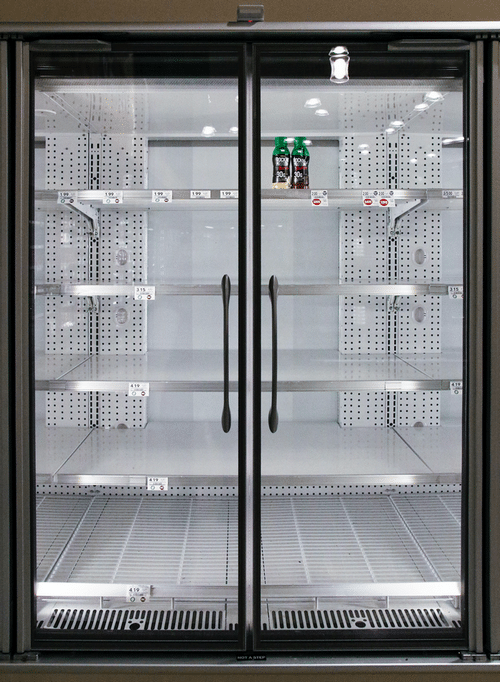

Refrigerator use in a veterinary clinic varies depending on the size and type of clinic. In small clinics, refrigerator use may be limited to providing ice for injured animals and vaccination.
Oftentimes, the clinic will also have a few food items like dog food and cat food. In larger clinics, refrigerators may be used for more extensive purposes such as holding and storing veterinary supplies or medications.
22-Boarding Cages

Cages are an essential piece of equipment in veterinary clinics for routine animal care. They provide a safe and secure environment for animals, preventing them from escaping and potentially harming others. Injured animals can recover in cages, which also prevent them from becoming prey. Cages also allow veterinarians to observe animals more closely and provide better care.
23-Lighting
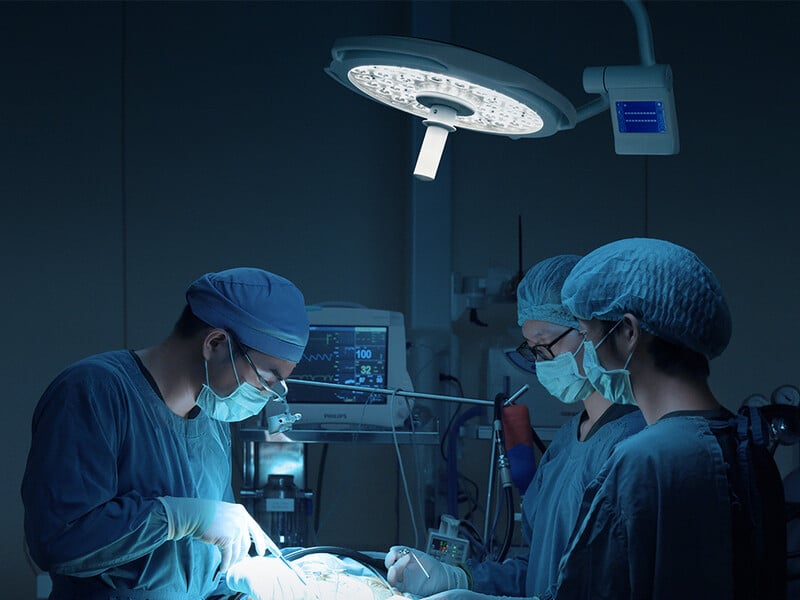
Lightning is needed in the exam room for treatment, surgery, and dental examination. In the past times, incandescent bulbs and halogen-based bulbs were used in veterinary clinics.
With the invention of LED-based lighting, the most critical change in the veterinary industry appears these lights are highly efficient, ecofriendly, have an extended life, and high cooling output.
These LED lights have a long life, the average rated life of these LED is 50,000 hours, and they use about half the electricity of their counterparts.
Other Tools
A selection of scissors and basic forceps is helpful in the consulting room, as is a range of nail clippers varying from heavy-duty (Great Dane) to tiny (canary). It is helpful to have a set of quiet electric clippers in the consulting room. The smaller quieter clippers are particularly useful and upset animals much less than standard clippers. Cordless clippers are more practical and do not present a trip hazard. All clippers should be cleaned thoroughly and disinfected between patients. Tools for taking samples (e.g. swabs, blood tubes, sample containers), microscope slides and coverslips should all be to hand. Examination gloves should include non-latex gloves for any members of staff with a latex allergy. Extra Tools:
- Otoscope
- Refractometer
- Hemocytometer
- Muzzles
- Nail Clippers and Electric Clippers
- Disposable syringes
- Dose syringe
- Needles
- Matic dose syringe
- Oral calf drencher
- Balling gun
- Frick Speculum
- White Nail trimmer
- Fecal loop
- Bull ring
- Electric dehorner
- Burdizzo castrator
- Fetal extractor
- Trocar and cannula
- Sphygmomanometer
- Blow dart
- Insemination kit
- Suction Machine
For More Vet Equipment & Tools Download This PDF Guide:
Conclusion
We have mentioned a complete List of Veterinary Tools and Equipment For Veterinarians In All Types of Veterinary Practices: Essentials and Extra Tools. Along with them, proper knowledge is also very important. To be aware of new technologies and tools, it is important to read Read a Lot of Veterinary Books.
Tip
Do You Want To Increase Your Veterinary Knowledge and Practical Skills?
You Can Now Download +3000 Veterinary Books Online In All Veterinary Fields.
Register Now

















 If you are planning to establish your own veterinary clinic or hospital, there is a
If you are planning to establish your own veterinary clinic or hospital, there is a













































![Ettinger’s Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine 9th Edition [PDF+Videos] Ettinger’s Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine 9th Edition [True PDF+Videos]](https://www.vet-ebooks.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/ettingers-textbook-of-veterinary-internal-medicine-9th-edition-100x70.jpg)





