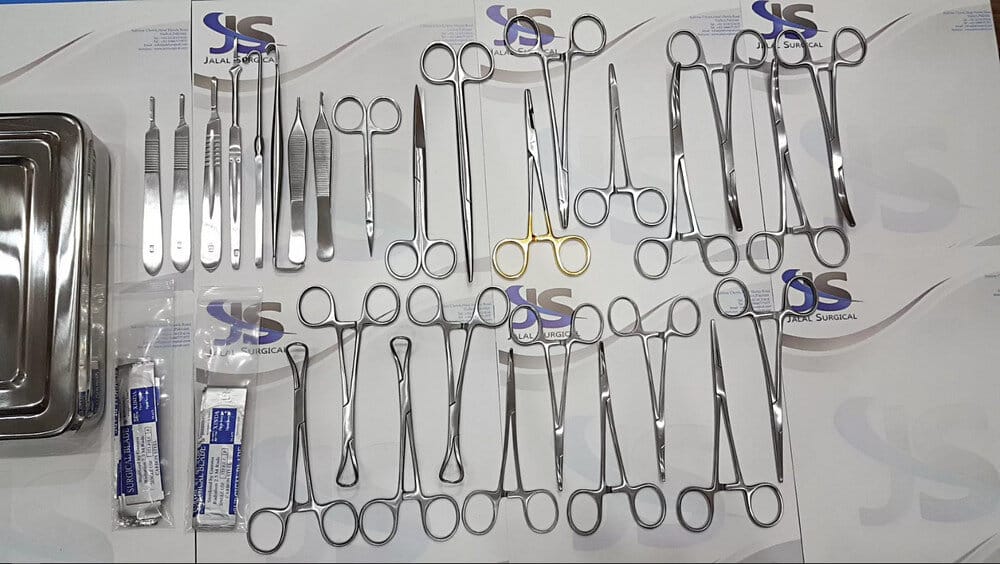
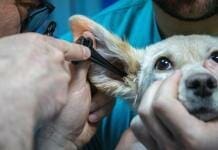
As a Completion To the Previous Article about Veterinary Equipment and Tools List, In this blog post, we will take a look at some common Veterinary Surgical Equipment List With Names, Uses, and Pictures in veterinary clinics.
Veterinary surgery is an important branch of veterinary medicine, we can’t begin learning veterinary surgery without knowing all the surgical tools you will use in any surgery that’s why we make this Veterinary Surgical Instruments List for all veterinary students to know all Veterinary Surgical Instruments List or veterinarians have come across the issue of needing to purchase surgical instruments for clinics.
???? General Surgical Instruments
General veterinary surgical instruments are the basic tools used in all operations. These instruments must be manufactured with high precision and years of experience to ensure the best results. Similarly, the user must be well-trained and experienced to achieve optimal surgical outcomes.
Below are commonly used general instruments in veterinary surgery:
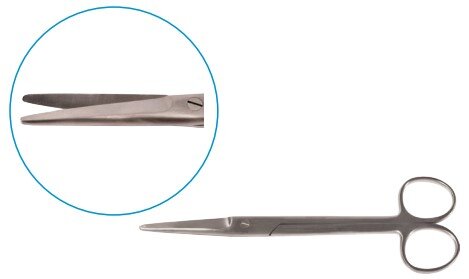
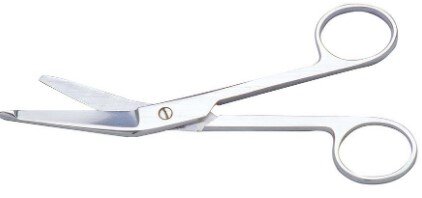
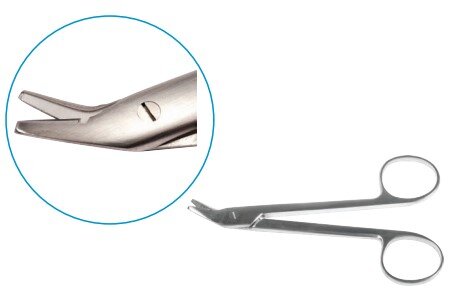
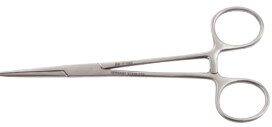
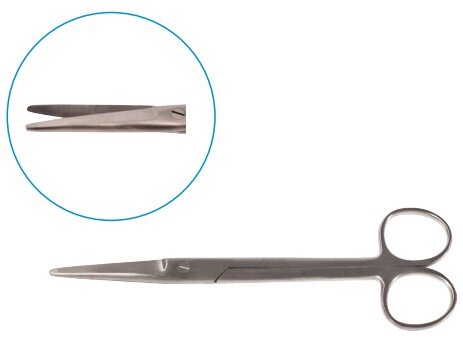
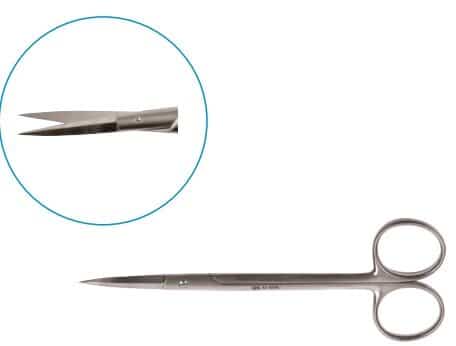
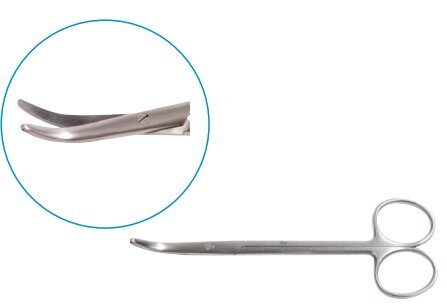
Scissors
Scissors are essential tools used by surgeons to cut and dissect tissues, muscles, organs, and sutures. They allow for the fast and safe removal of obstructive tissues during procedures. Made from balanced stainless steel, surgical scissors are thinner, sharper, and pointed for precision cutting.
Forceps
Forceps are essential surgical tools used to hold tissues, separate structures, improve access, and assist in cutting and suturing. They are also used for tweezing and applying pressure during procedures.
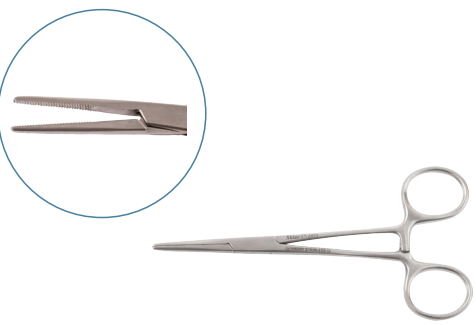
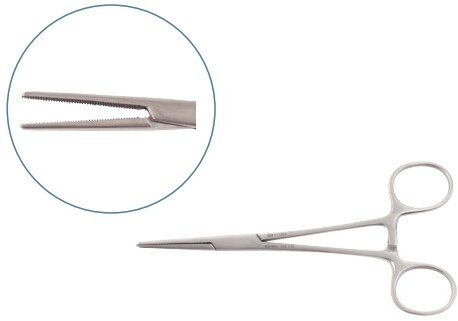
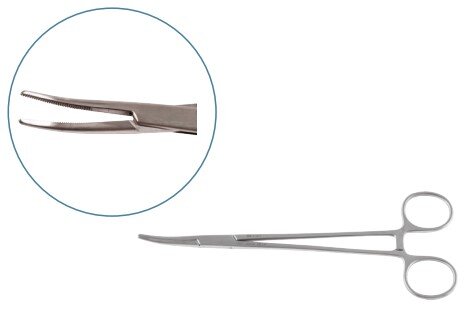
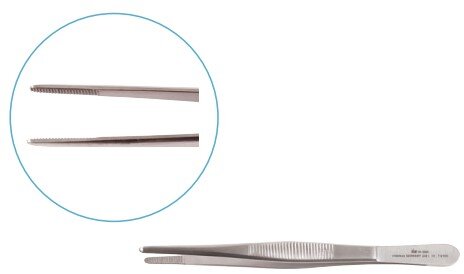
Dissecting Forceps
Dissecting forceps are temporary tools used to handle skin, tissues, and organs during surgery. Surgeons also use them to guide needles or manipulate delicate structures.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Standard plain & toothed | Handle soft tissues |  |
| Mosquito | Hold small capillaries |  |
| Adsons | Handle soft tissues |  |
| Continental Standard | Handle skin |  |
| Emmett | Handle deep tissues | 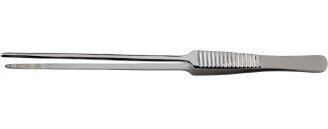 |
| Debakey | Handling of viscera |  |
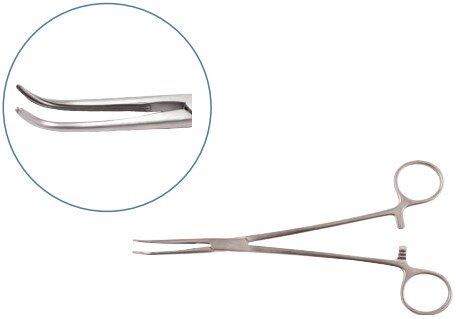
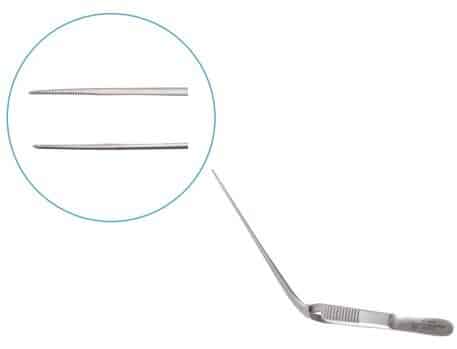
Tissue Forceps
Tissue forceps are used for delicate manipulation of tissues without causing trauma. They provide secure grip and precise handling of soft organs and structures during surgical procedures.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Babcock | Handling viscera and soft tissue | 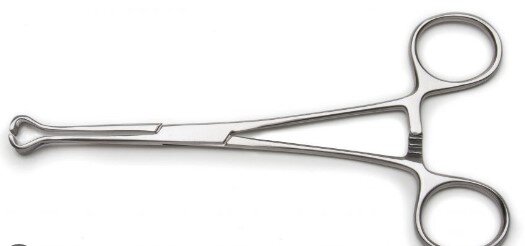 |
| Allis | Handling soft tissue |  |
| Duval | Handling viscera and tissue | 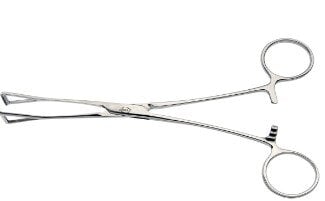 |
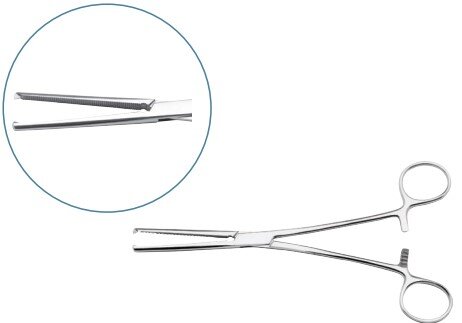
Clamps or Hemostats
Hemostats are essential surgical instruments used to occlude blood vessels either completely or partially. They help control bleeding during surgery and are commonly used to block blood flow to internal organs temporarily to protect them during procedures.
Visceral Clamps
Used to occlude visceral organs like the stomach, intestines, or cervix.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Doyen Mayo Robinson | Occlusion of stomach and intestine |
 |
| Parker Kerr | Occlusion of cervix |
 |
Towel Clamps
Used for securely attaching surgical drapes to the patient’s skin.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Cross Action | Attach drapes to the surgical area |
 |
| Backhaus | Attach drapes to the surgical area |
 |
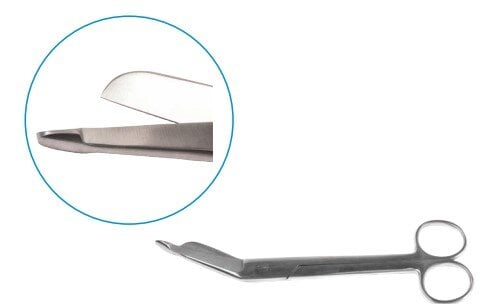
Scalpel
The scalpel is a long, thin surgical instrument used to make precise cuts in the skin and underlying tissues. It is an essential tool in dermatology and surgery, enabling incisions, tissue dissections, and various surgical techniques. The term “scalpel” originates from Latin, meaning “small knife.” Scalpels come in a range of sizes and shapes, each suited for specific procedures.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Scalpel Handle | Hold surgical blades |
 |
| Scalpel Blades | Make incision and tissue transection |
 |
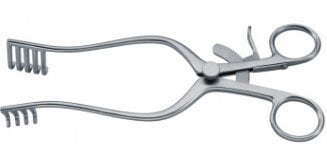
Retractors
Retractors are used to hold open the incision or wound during surgery, allowing the surgeon better visibility and access to the surgical site. They help retract soft tissues, joints, or organs out of the way, and can be manually held or self-retaining to free the surgeon’s hands.
Manual Retractors
These retractors require manual handling to maintain exposure of tissues and surgical fields.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Langenbeck | Soft tissue retraction |
 |
| Volkman | Retraction of tendons and muscles |
 |
| Hohman | Retraction of joints |
 |
| Czerny | Soft tissue retraction |
 |
Self-Retaining Retractors
These retractors do not require constant holding and are designed to hold the tissue apart automatically, keeping the surgical field open.
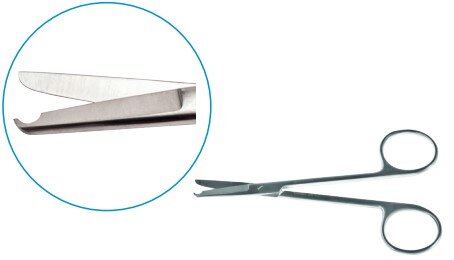
Needle Holder
A needle holder, also known as a needle driver, is a surgical instrument designed to securely hold suturing needles. It features a comfortable handle for one-handed use and a shaft with a tip that guides the needle through tissues with precision. Some types also incorporate built-in scissors for cutting sutures.
| Type | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Gillies | Hold needle and cut suture |  |
| Olsen Hegar | Hold needle and cut suture | 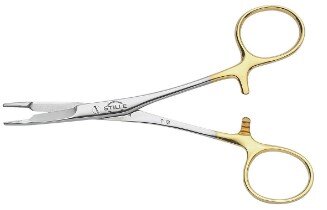 |
| Mayo Hegar | Hold needle |  |
| Bruce Clarke | Hold needle |  |
| McPhail | Hold needle | 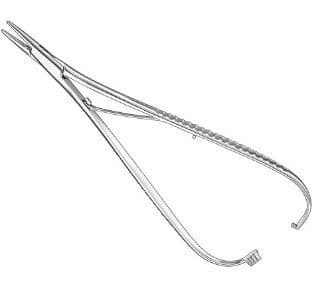 |
???? Specific Surgical Instruments
The surgical instruments used by veterinarians during operations must be of the highest quality due to the fragility of organs and bones. Even minor negligence can lead to severe damage. That’s why top-grade, specially designed tools are crucial in veterinary practice.
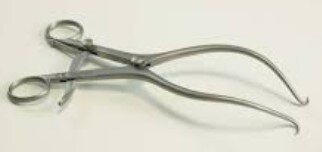
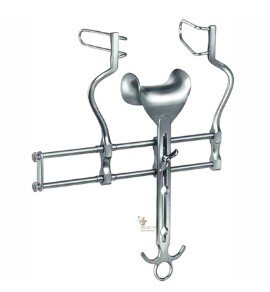
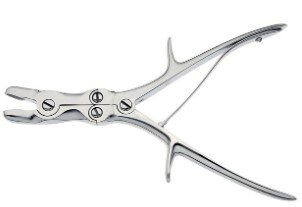
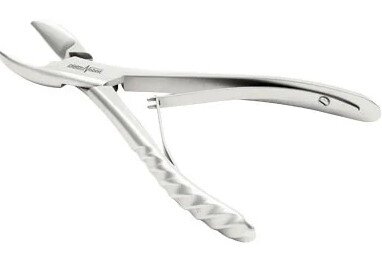
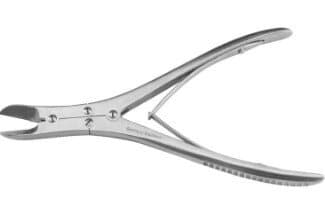
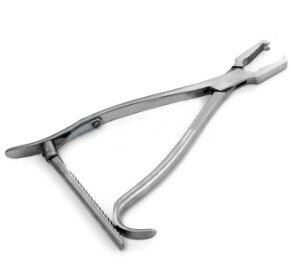
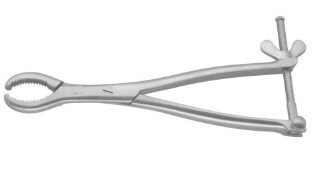
Orthopedic Surgical Equipment
Orthopedic instruments are used by surgeons to diagnose and treat bone fractures, cut or remove bone, and perform orthopedic procedures. These tools are precision-crafted for efficient and safe handling of skeletal structures.
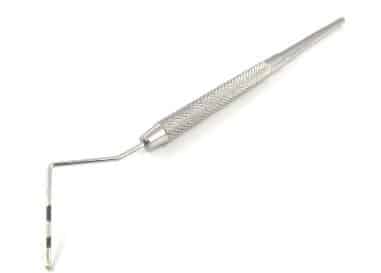
Ophthalmic Surgical Instruments
Ophthalmic surgical tools are used for carrying out eye-related surgeries. Both cornea and lens-related surgeries are done with the help of different surgical instruments.
Scissors
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Iris scissors | To cut iris |
 |
| Castroviejo scissors | Cut lens capsule |
 |
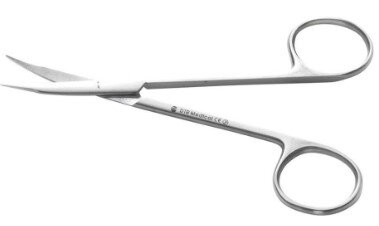
| Tenotomy scissors | For fine dissection |
 |
Forceps
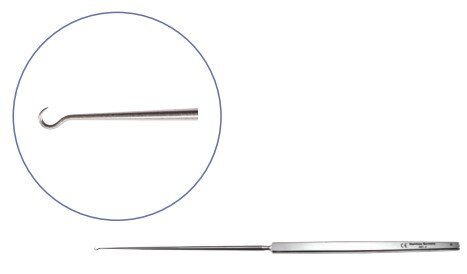
Hooks
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Kirby expressed hook | Use for lens removal |
 |
Speculums
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Williams speculum | Provide access to eyeball by a retraction |
 |
| Barraquer speculum | Provide access to eyeball by a retraction |
 |
Dilators
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Nettleship dilator | Dilate narrow canals |
 |
Needle Holder
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Castroviejo needle holder | Hold needle during suturing |
 |
Dental Instruments
Dental instruments are very important for every single dental surgery. They are the most common tools used by vets for the diagnosis and treatment of oral problems—such as removing dental calculus, repairing teeth, and performing extractions. Instruments like scalers, elevators, curettes, and chisels each serve specific functions. Below are commonly used dental surgical instruments:
Teat Instruments
Cows play a crucial role in dairy farming by providing milk, an essential dietary component. However, their teats are prone to damage or infections, which can hinder milk production. Teat surgical instruments are used to treat these issues effectively and maintain udder health. Below are common teat surgical tools:
Plastic Surgery Instruments
Plastic surgery is a form of body modification that can be approached for a myriad of reasons – whether it is for someone who wants to improve their appearance or for someone who needs to reconstruct parts of their body that have been damaged by injury or disease…
Clamps
Forceps
Scissors
Evacuation Instruments
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Frazier suction tube | Remove debris and fluid from surgical spaces |
 |
| Adson suction tube | Aspire blood and residues |
 |
| Baron suction tube | Remove fluid and debris |
 |
Retractor and Exposure
Gastrointestinal Instruments
The digestive system is an important part of the body! It’s responsible for taking in nutrients from your food and turning it into energy. The upper GI tract (esophagus, liver, stomach, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, diaphragm) and the lower GI tract (small and large bowel, mesentery, appendix, rectum, omentum, anus) each require specialized surgical instruments. Upper‑GI tools are medium‑length; lower‑GI tools are long or extra‑long.
Cholecystectomy Instruments
Liver & Stomach Surgical Instruments
Lower GIT Instruments
Rectal & Anal Instruments
Cardiothoracic And Vascular Surgical Instruments
In the field of cardiothoracic surgery, common procedures include coronary artery bypass grafting and aortic valve replacement. Although approaches and incisions differ, surgical training and expertise are key to outcomes. Advances in medical equipment have given surgeons specialized tools to remove vessels, repair valves, and perform bypasses with greater precision and safety.
Clamps & Related Instruments
Probes & Dilators
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Garrett vascular dilators | Perform vessel dilation |  |
Measuring Instruments
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Tessier caliper | Measure anatomical structures |  |
Installation & Evacuation Instruments
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Wolf suction | Remove blood from surgical site |
 |
| Poole suction tube | Remove large volumes of fluid |
 |
Retraction & Exposure
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Allison retractor | Retract lungs |
 |
| Malleable ribbon retractor | Retract during orbital dissection |
 |
| Leaflet retractor | Used in cardiac surgery |
 |
Special Instruments
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
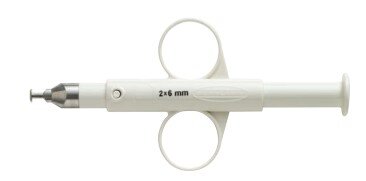
| Vessel punch | Create an opening in vessels |
 |
| McIntosh suture holder | Separate sutures |
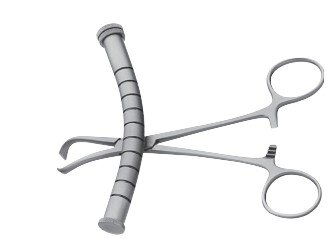 |
| Rummel tourniquet | Occlude blood vessels |
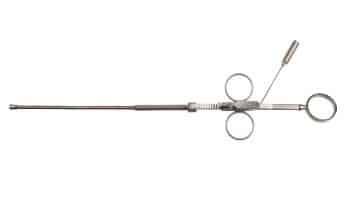 |
Endoscopic Instruments
Endoscopy is used in animals to examine internal organs via a camera, either diagnostically (viewing the digestive tract through mouth or anus) or therapeutically (removing foreign objects, repairing abnormalities). Under general anesthesia, veterinarians can visualize the heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, and more. Endoscopy improves recovery by avoiding large incisions.
Essential Endoscopic Instruments
Viewing of Working Space
Special Instruments
| Instrument | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Chitwood DeBakey clamp | Clamp lung tissues |
 |
| Dennis clamp | Hold tissues |
 |
| Chitwood suture cutter | Cut sutures |
 |
Other Equipment
Below are additional miscellaneous instruments commonly used in various veterinary surgical procedures.
| Instrument | Use | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Cusco Vaginal Speculum | Exposure of vaginal tissue |
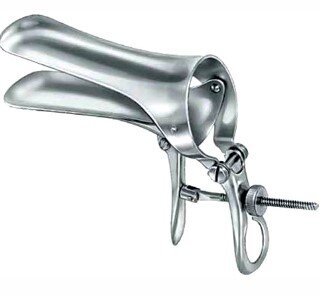 |
| Rampley Sponge Holding Forceps | Hold swabs and sponges |
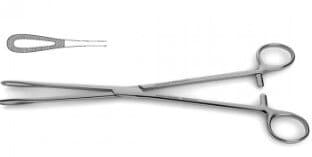 |
| Hartman Crocodile Forceps | Nasal and oral use |
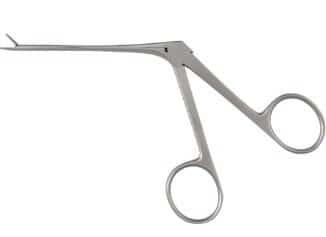 |
Conclusion
There are many reasons why surgical instruments are needed in surgeries. First, they are used to cut and pierce the skin. Second, they are used to perform the operation. Third, they are used to remove foreign objects. Fourth, they are used to keep the patient from bleeding. So that’s why we need surgical instruments for surgeries. We hope you enjoyed our article about surgical instruments. You may have never thought about it, but there are a lot of different instruments that are used in surgeries. Understanding the different instruments and what they are used for will help you appreciate the skill and expertise of veterinary surgeons. Since there are so many different instruments used in surgeries, it can be difficult to keep track of them all but we have mentioned the most important ones.
Do You Want To Increase Your Veterinary Knowledge and Practical Skills?
You Can Now Browse and Download +3000 Veterinary Books Online In All Veterinary Fields.
Register Now